Relations
What is a Relationship and their role in the data model?
Section titled “What is a Relationship and their role in the data model?”A Relation its a logical link between records, is the way of saying some record X has something to do with record Y, the way they are related and what that relation represents depends
on the configurator user, but the most common use cases is to express parent to child relationships or categorization with atomic records.
Examples:
- A
Productrecord related to aCategoryrecord to express something like a ProductShoeshas a relationCategoryassigned to the Category recordGarment- A list of
Itemrecord related to anInvoicerecord, to express items being sold in a particular transaction, likeInvoice 1having 10Black ShoesItems
To summarize its the way of relating atomic units of data together based on their nature, to keep track of the interactions your particular data model requires
Types of relationships supported
Section titled “Types of relationships supported”The relationships you can create in DatAscend are named after the types on relational database
One To One (1:1)
Section titled “One To One (1:1)”To express that a given entity record can only have one possible value for the related entity record, and in the same way, that related entity record cannot be referenced in this same relationship by a different entity record.
- Example: A Product can only have 1 Owner, and that Owner is not allowed to own more than one Product
One To Many (1:M)
Section titled “One To Many (1:M)”To express that a given entity record can have multiple related records from a different entity.
- Example: A Car entity can have many Parts records, like each Part entity record being: heated seats, airbags, etc…
Many To One (M:1)
Section titled “Many To One (M:1)”This is the most common relation, its basically the inverse of the One To Many, its a way of saying that multiple records of a given entity can all be related to the same record in a related Entity.
- Example: Many Students entity records can be assigned to the same School record.
Many To Many (M:M)
Section titled “Many To Many (M:M)”This is the most abstract relation we support, and its the most versatile one, used to express that many records of a given entity record can be related to many records of a related entity. Used most of all to related reusable non uniquely owned entities between each other.
- Example: Many Students entity records can be assigned to many Courses records, and in the same way, each Courses record will have many students related.
How to create a new relationship?
Section titled “How to create a new relationship?”- The place to create, edit or generally manipulate Relations is the Studio. To enter it you can simply click the
Studionavigation item on the header of the page.
Note:
- You need to be assigned to an Administrator role in order to see or even access the Studio
- If you are on the welcome page, you can also click the
Studiocard
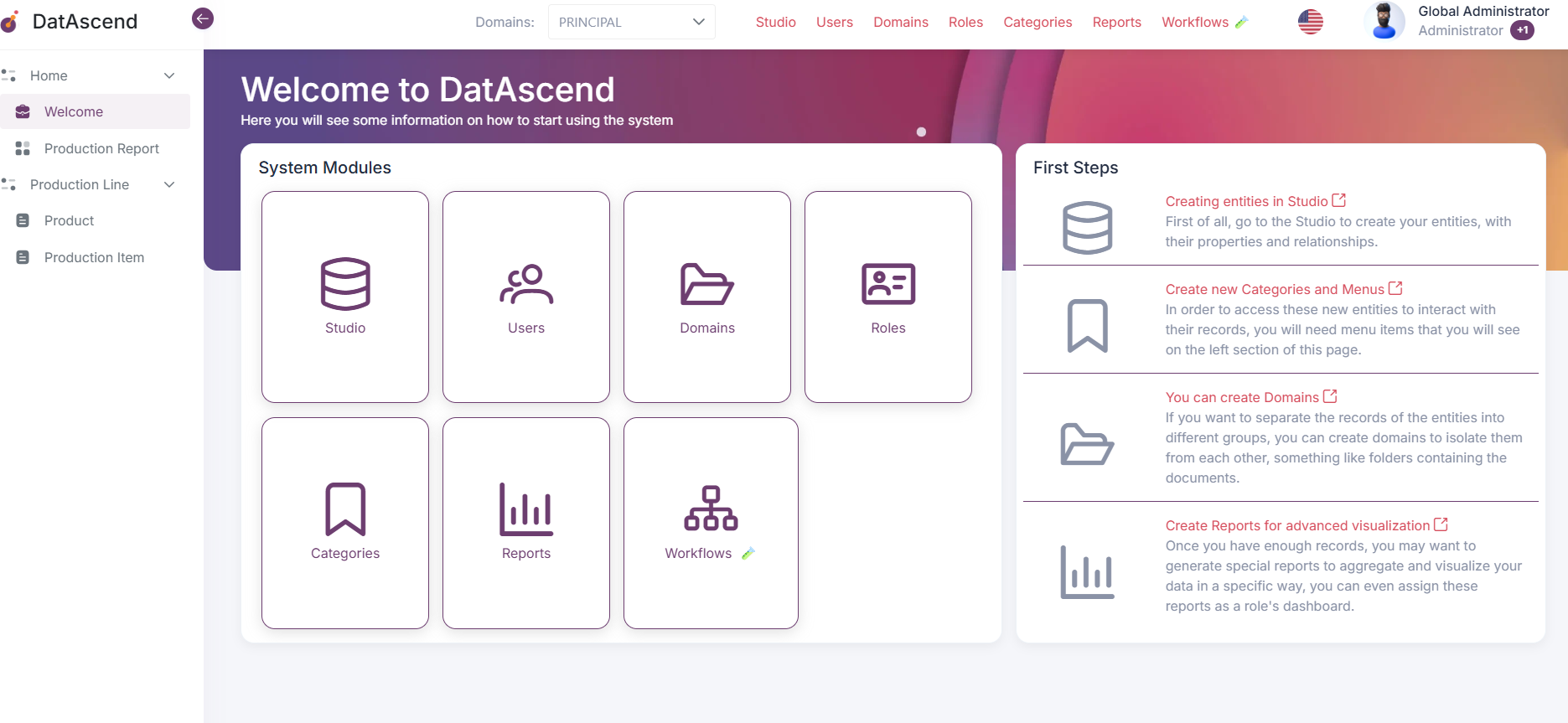
- Once on the
Studioclick on the Entity wether in the left side bar that lists them, or the card in the canvas, that will show the details drawer
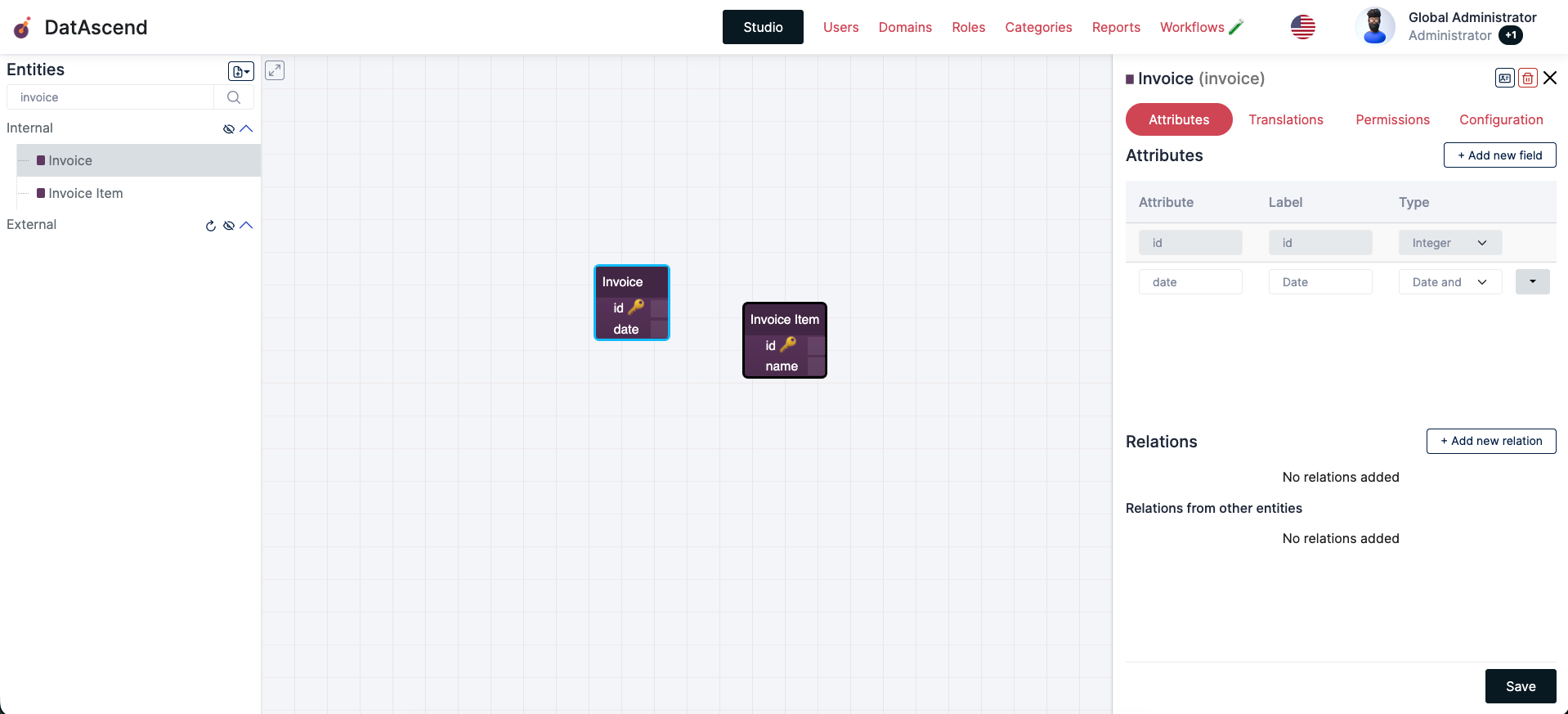
- On the details drawer, focus on the
Relationssection and click the+ Add new relationbutton, which will show theAdd Relationmodal
-
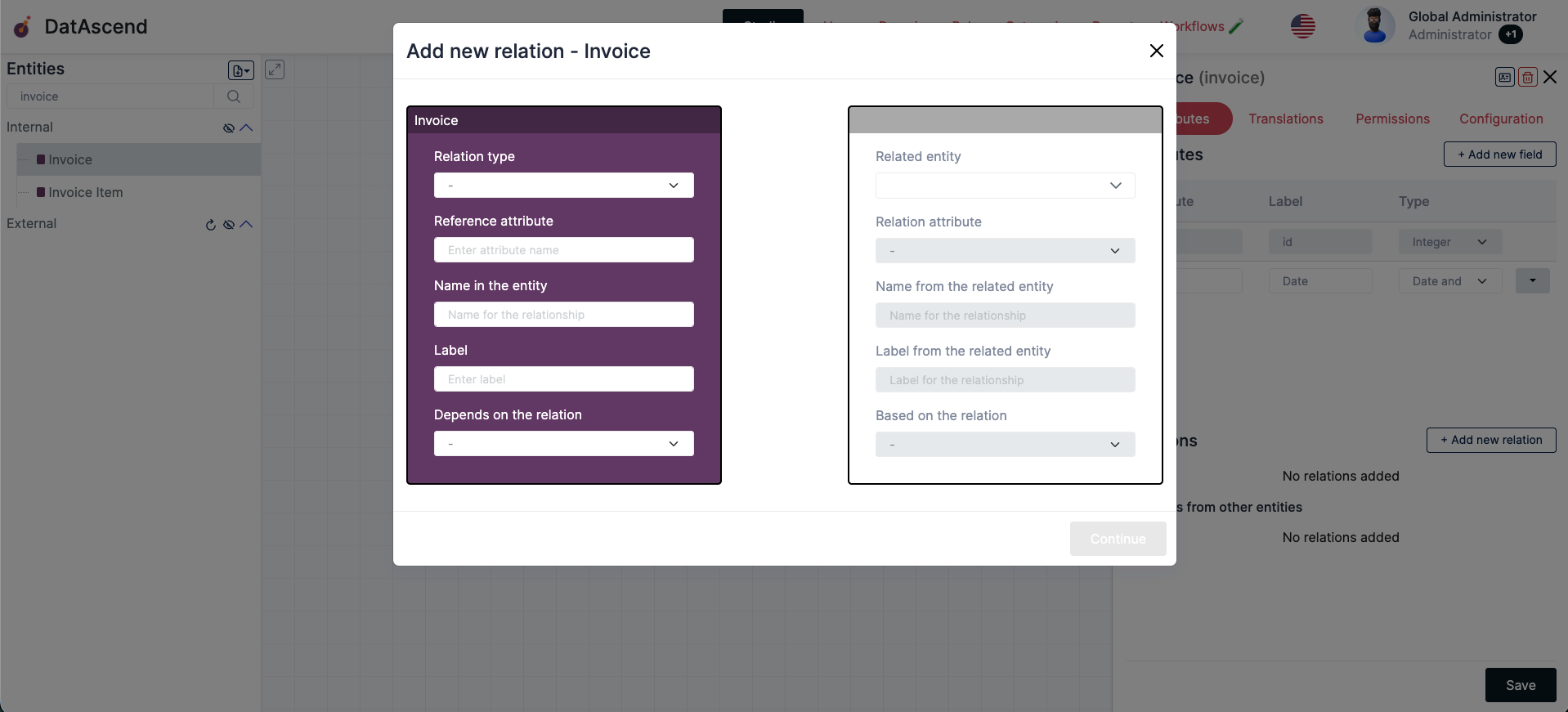
In here you can create a new relationship, the constrols will change a little based on the relation type you want to create, but here we will explain what every field is for:
For the Entity
Section titled “For the Entity”Relation type
Section titled “Relation type”- The type of the relation, as described on the Types of relationships supported
Reference attribute
Section titled “Reference attribute”- The attribute on the Entity to use as a reference for the relation, there are two possible cases in here:
- a. The relation type is
One To OneorMany To One: The input will be a text field, where you can write the property where the related reference value will be stored in the entity record - b. The relation type is
One To ManyorMany To Many: The input will be a dropdown field, where you have to pick the existing attribute on the entity, that the related entity will be referencing
- a. The relation type is
Name in the entity
Section titled “Name in the entity”- The sanitized name this relation will have on the main entity, used to perform updates to the relations
- The human friendly name you can give to this relation, it will be displayed when interacting with their records
Depends on the relation
Section titled “Depends on the relation”- In the case of a direct dependency between relations, you can select a second relation in the main entity, that this new relation will depend on, more on dependeny in Dependency
For the Related Entity
Section titled “For the Related Entity”Related entity
Section titled “Related entity”- The related
Entityon the other end of this relationship
Relation attribute
Section titled “Relation attribute”- The attribute on the
Related Entityto use as a reference for the relation, there are two possible cases in here:- a. The relation type is
One To One,Many To OneorMany To Many: The input will be a dropdown field, where you have to pick the existing attribute on the related entity, that the main entity will be referencing - b. The relation type is
One To Many: The input will be a text field, where you can write the property where the main entity reference value will be stored in the related entity record
- a. The relation type is
Name from the related entity
Section titled “Name from the related entity”- The sanitized name this relation will have on the related entity, used to perform updates to the relations
Label from the related entity
Section titled “Label from the related entity”- The human friendly name you can give to this relation, it will be displayed when interacting with their records of the related entity
Based on the relation
Section titled “Based on the relation”- In the case of a direct dependency between relations, you can select a second relation in the related entity, that this new relation will depend on, more on dependeny in Dependency
-
Confirm the changes and then click save on the details drawer to create the relationship
Dependency
Section titled “Dependency”There are cases when some ralations possible values depends on another relation current value, we call these scenarios Dependency or Dependency Relations. The easiest way to ilustrate
it is with some examples:
- For the entities
Animal,Animal Type,Animal Breedrelated in the following way
Animal Breedhas a relation withAnimal TypeAnimalhas a relation withAnimal Typeand one inAnimal Breedwith a Dependency onAnimal Typewhere theAnimal Breed’s type matches the values on the type- And the following records
Animal Type-> DogAnimal Type-> CatAnimal Breed-> Persian, withtypeCatAnimal Breed-> Bulldog, withtypeDog- When creating a new
Animalthe user picks thetypeas Dog, the options forAnimal Breedshould be filtered out based on that value, so only “Bulldog”, would be available- In constrast, when the user picks the
typeas Cat, the options would be “Persian”
NOTE:
Dependencyrelations are currently not enforced on Many to Many relations
How to view existing relationships for an entity?
Section titled “How to view existing relationships for an entity?”-
The place to view, edit or generally manipulate Relations is the Studio. To enter it you can simply click the
Studionavigation item on the header of the page.
-
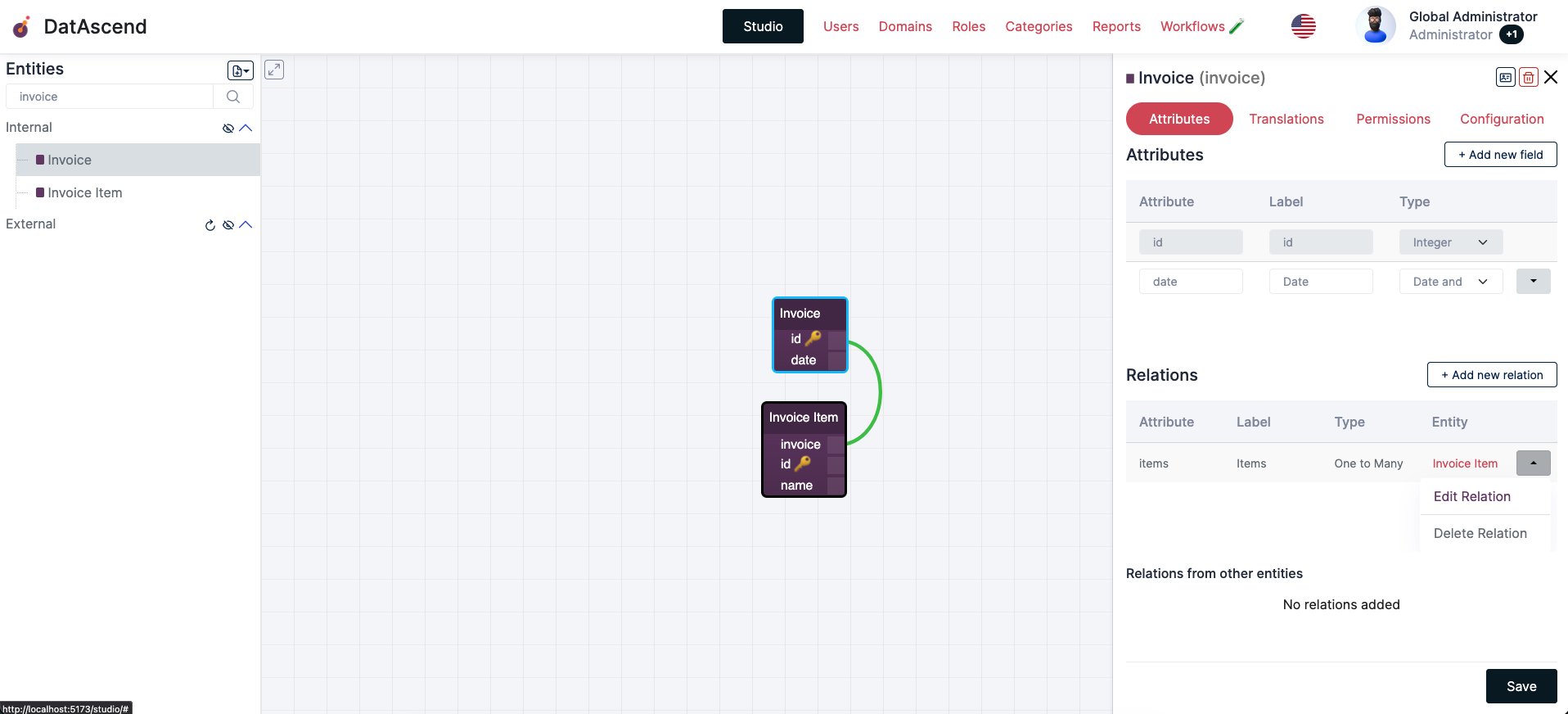
Once on the
Studioclick on the Entity wether in the left side bar that lists them, or the card in the canvas, that will show the details drawer, clicking on an existing relation dropdown at the end will display the actions, to view the current state of the relation, click theEdit Relation
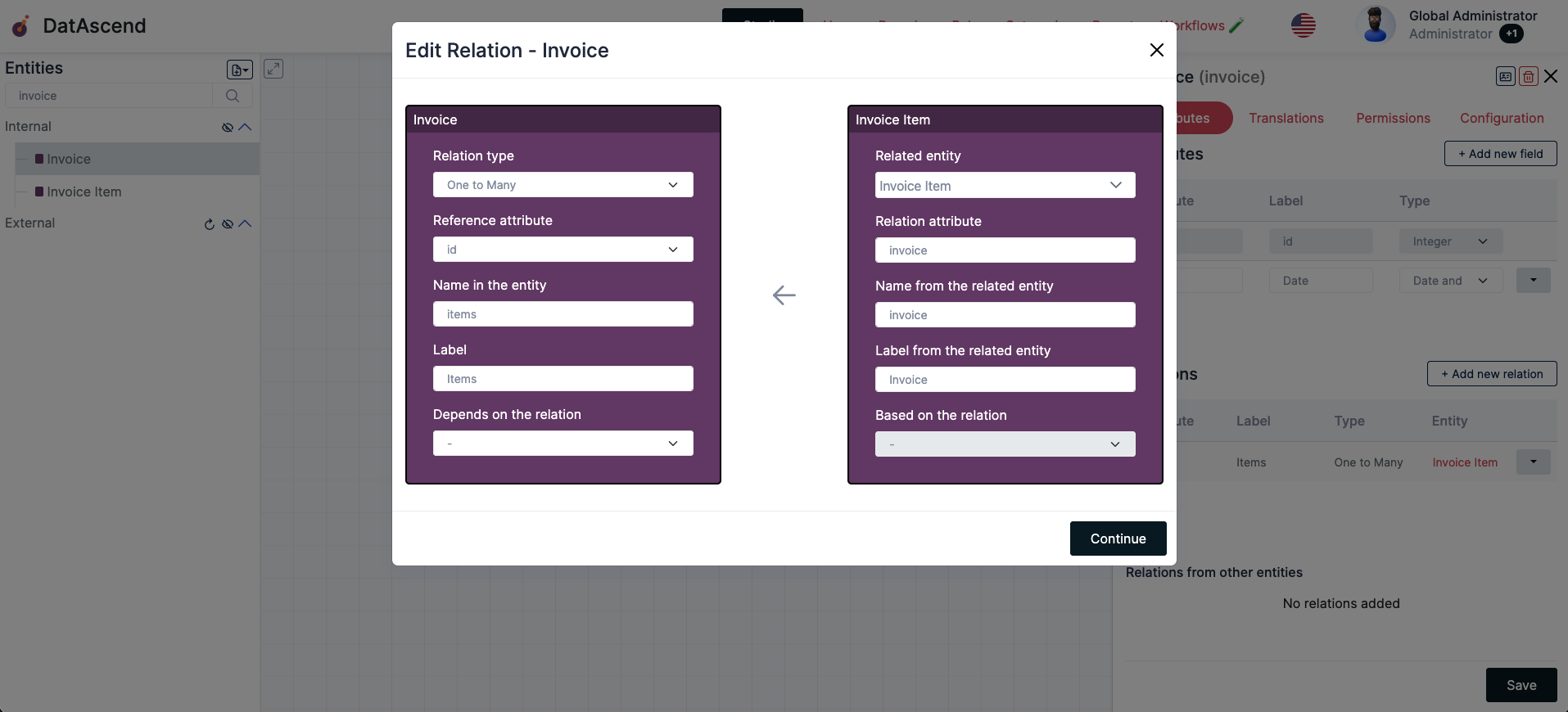
How to remove a relationship?
Section titled “How to remove a relationship?”-
The place to view, edit or generally manipulate Relations is the Studio. To enter it you can simply click the
Studionavigation item on the header of the page.
-
Once on the
Studioclick on the Entity wether in the left side bar that lists them, or the card in the canvas, that will show the details drawer, clicking on an existing relation dropdown at the end will display the actions, to view the current state of the relation, click theDelete Relation

- Confirm the changes and then click save on the details drawer to delete the relationship
How to use the UI to navigate between related entities
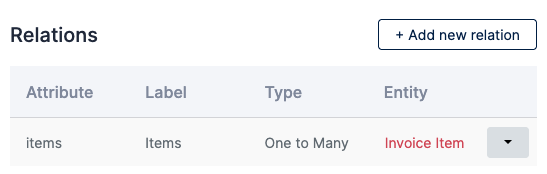
Section titled “How to use the UI to navigate between related entities”On the details drawer in the Studio, you can see the Relations section, and each row has a column Entity that its in itself a link to that entities details drawer, clicking it will
select that other entity and its attributes and relations. This way you can traverse the whole relation graph just with clicks
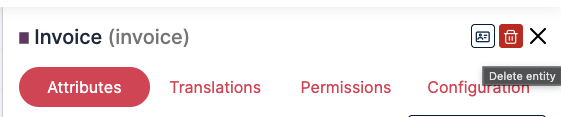
Deleting entities
Section titled “Deleting entities”Delete entities can also be done from the studio, entering the details drawer, there will be a button on top right corner, with a trash can icon
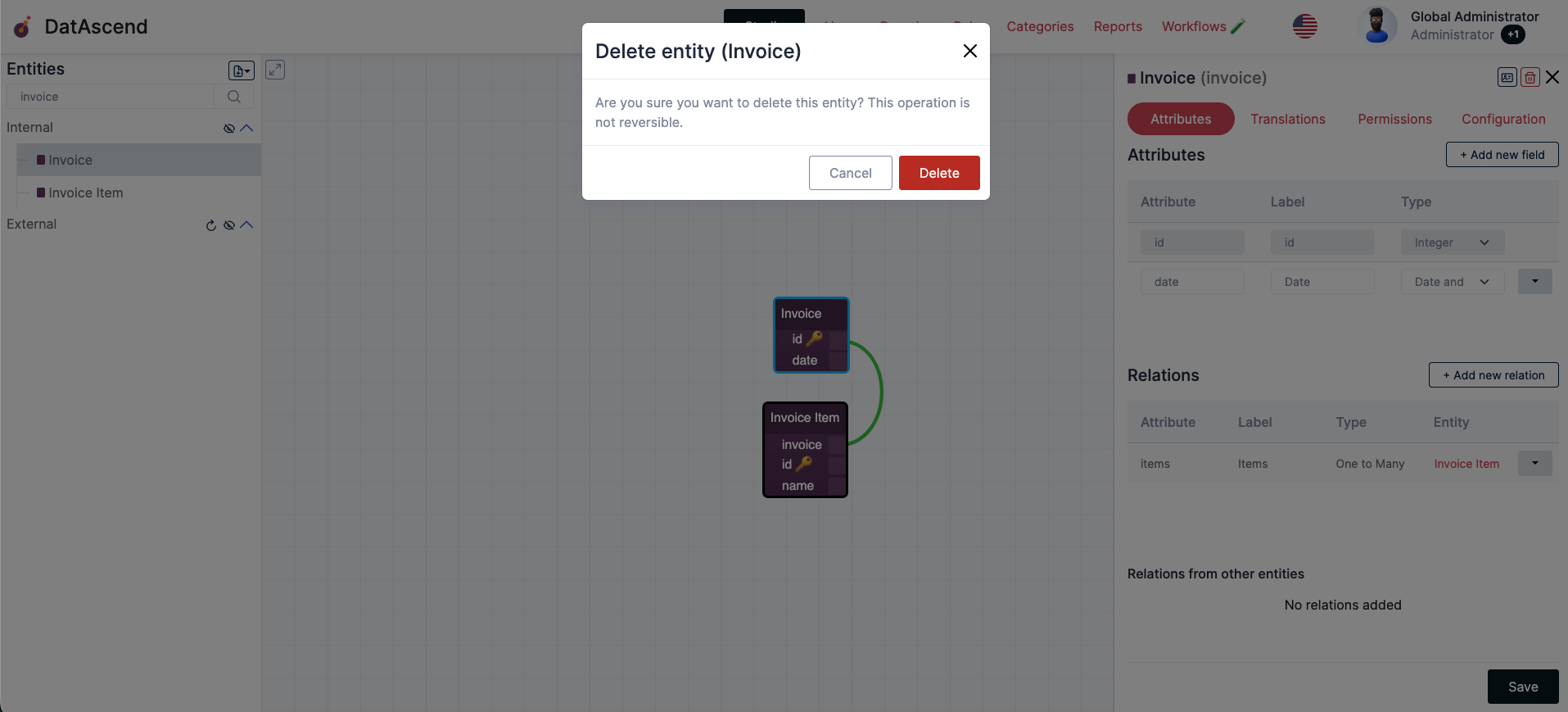
Confirm the deletion of the entity to complete
Best practices and common mistakes to avoid
Section titled “Best practices and common mistakes to avoid”Circular references
Section titled “Circular references”Currently we don’t support circular references, having entities related to itself its discouraged as we don’t officially support it